Do not assume that Google cannot manage JavaScript – the results of a series of tests conducted by Merkle | RKG prove otherwise. The tests aimed to investigate the extent to which different JavaScript functions are crawled and indexed by Google.
Google’s ability to execute JavaScript and read the document object model (DOM)
The capability of Google to crawl JavaScript dates back to 2008, although it may have been limited at that time.
Today, it is evident that Google has advanced not just in terms of the types of JavaScript they crawl and index, but also in terms of producing fully functional websites.
The technical SEO team at Merkle was interested in learning more about the kinds of JavaScript events that Googlebot might crawl and index. We discovered some unexpected findings and established that Google not only processes various JavaScript event types but also indexes dynamically created content. How? Google is analysing the DOM.
The DOM: what is it?
Not many SEOs are familiar with the DOM or the Document Object Model.
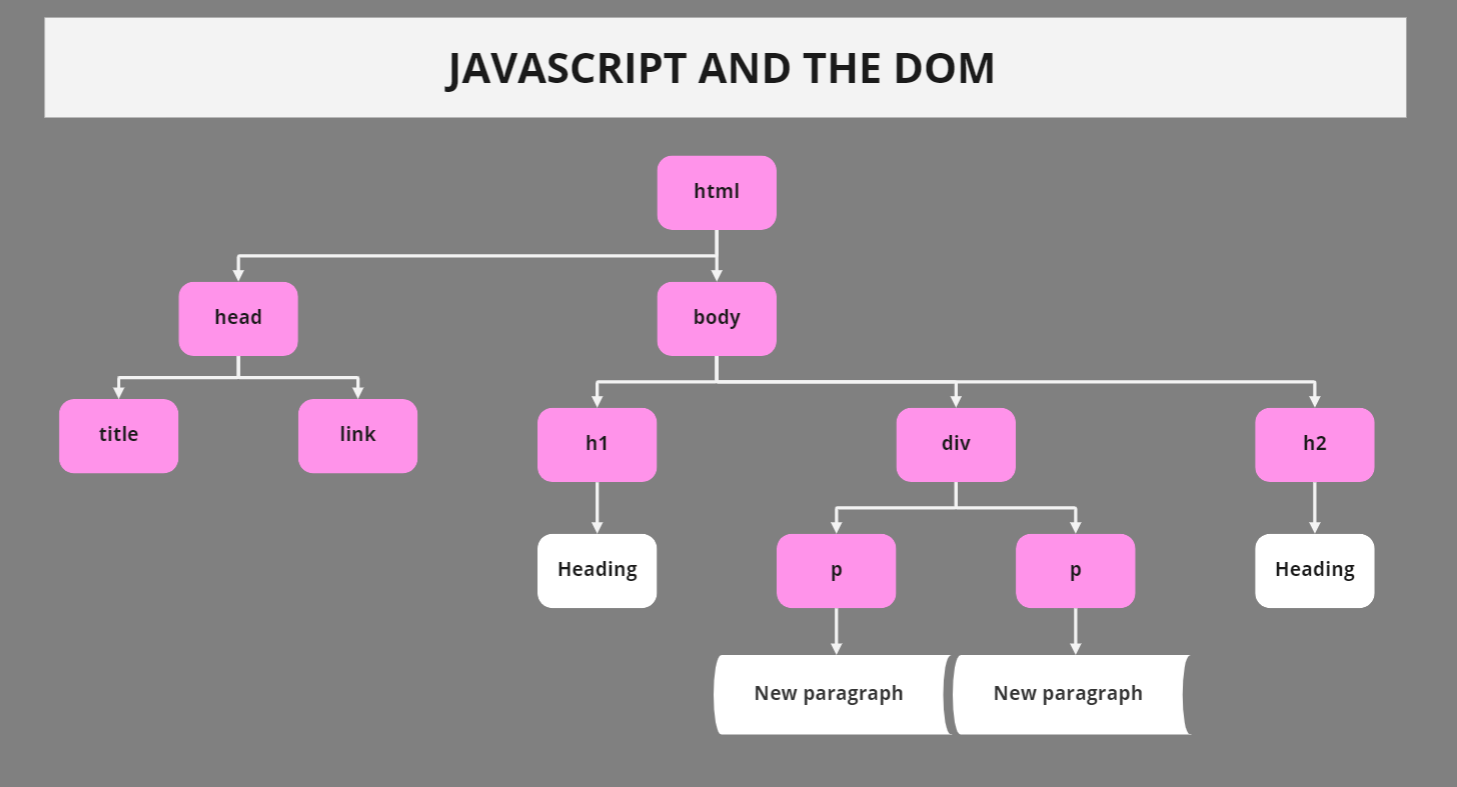
The illustration below demonstrates what happens when a browser requests a web page, and how the DOM is involved.

The DOM, as it is used in web browsers, can be defined as API (application programming interface) for markup and structured data such as XML or HTML.
The DOM also specifies how that structure may be accessed and modified. The Document Object Model is an API that is independent of any particular programming language, but it is mostly used in web applications with JavaScript and dynamic content.
The DOM is the interface, or the “bridge,” between programming languages and web pages. The DOM is the content of a web page, not (only) source code. This makes it crucial.
Below you can see how JavaScript works with the DOM interface.
We were excited to learn that Google could read DOM documents, and understand signals, and content that was dynamically added, including title tags, page text, header tags, and meta-annotations like rel=canonical. Keep reading for more details.
The tests and their outcomes
To investigate how various JavaScript functions would be indexed and crawled by Googlebot, we developed several tests. Controls were established to guarantee that activity to the URLs would be recognised independently. Let us review a couple of the test findings that caught our attention in greater detail below. They are separated into five groups:
- JavaScript redirects
- JavaScript links
- Dynamically inserted content
- Dynamically inserted metadata and page elements
- An essential example with rel=“nofollow”
JavaScript redirects
To assess common JavaScript redirection, we first changed the way the URL was displayed. We agreed on using the window.location function. There were two tests run: The window.location method in Test A used the absolute URL property. And in Test B we used Relative URL.
The result: Google immediately followed the redirects. From an indexing perspective, these were read as 301s — the end-state URLs replaced the redirected URLs in Google’s index.
In a second test, we used an authoritative page and established a JavaScript redirect to a new page on the website with the exact same information. For popular key phrases, the original URL ranked on Google’s front page.
The result: As predicted, Google followed the redirect and removed the old page from its index. The updated URL was promptly indexed and given the same search engine ranking for identical queries. This caught us off guard and appears to show that JavaScript redirects can function just like permanent 301 redirects in terms of rankings.
JavaScript redirects for site moves may no longer be a cause for concern, as our findings suggest the transfer of ranking signals in this scenario. This is supported by Google’s guidelines, which state:
The usage of JavaScript to redirect users is a legitimate practice. For example, you may use JavaScript to redirect users to an internal page once they have logged in. Consider the intent while reviewing JavaScript or other redirect mechanisms to verify your site complies with our guidelines. When relocating your site, 301 redirects are preferred, however, if you do not have access to your website’s server, you might use a JavaScript redirect.
JavaScript links
We evaluated numerous different JavaScript links that were coded in various ways.
Dropdown menu links were examined. These connections have always been difficult for search engines to consistently follow. We conducted a test to see if the onchange event handler would be executed. It is significant that this is a particular kind of execution point since, unlike the JavaScript redirection above, we are asking for interaction to change something.
The result: The links were fully indexed and followed.
We also tried typical JavaScript links. These are the most frequent forms of JavaScript links that SEOs have typically advised should be converted to plain text. These tests involved JavaScript URLs created with:
- Functions outside of the a tag but called within the href AVP (“javascript:openlink()”)
- Functions outside of the href Attribute-Value Pair (AVP) but within the a tag (“onClick”)
- Functions inside the href AVP (“javascript:window.location“)
- And so on.
The result: The links were thoroughly crawled and followed.
The following test, similar to the onchange test before, looked at other event handlers. In particular, we were considering the concept of using mouse movements as the event handler and then disguising the URL using variables that are only activated during the event handler’s (in this example, onmousedown and onmouseout) firing.
The result: The links were crawled and followed.
Concatenated links: we needed to make sure Google was reading the variables in the code even though we knew they could execute JavaScript. In this test, we combined a series of characters that, when put together, formed a URL.
The result: The link was crawled and followed.
Dynamically inserted content
Dynamically added text, graphics, links, and navigation are undoubtedly significant. To fully comprehend the theme and content of a website, a search engine needs high-quality text content. The importance of SEOs staying on top of this has increased in the age of dynamic websites.
These tests were made to look for dynamically added text in two distinct scenarios:
- Check the search engine’s capacity to take into account text that has been dynamically added and is included in the page’s HTML code.
- Examine the search engine’s capability to take into account text that is dynamically introduced but not contained inside the page’s HTML code.
The result: The text was crawled, indexed, and the page was ranked for the content in both instances.
For additional information, we examined a client’s JavaScript-coded global navigation, with all links inserted with a document.writeIn method, and ensured they were completely crawled and followed. It should be highlighted that Google’s feature describes how webpages developed with the AngularJS framework and the HTML5 History API (pushState) may be generated and indexed by Google, ranking alongside traditional static HTML pages. This is why external files and JavaScript assets mustn’t be blocked from Googlebot access. Google is also probably moving away from supporting Ajax for SEO guidelines. Who needs HTML snapshots when you can just render the whole page?
Regardless of the content type, our testing showed the same outcome. For instance, when photos were loaded in the DOM, they were crawled and indexed. We even made a test where we dynamically produced breadcrumb markup for data-vocabulary.org and placed it into the DOM. Result? Successful rich snippets with breadcrumbs in Google’s SERP.
It should be noted that Google now advises JSON-LD markup for some structured data.
Dynamically inserted metadata and page elements
Several tags that are essential for SEO were dynamically inserted into the DOM:
- Meta descriptions
- Canonical tags
- Meta descriptions
- Title elements
The result: In every instance, the tags were crawled respected and behaved as HTML source code components should.
We will learn more about precedence through an intriguing follow-up test. Which signal prevails when there are contradictory ones? What happens if there is a noindex,follow in the DOM and a noindex,nofollow in the source code? This will be covered in the next thorough testing. Our studies, however, revealed that Google can ignore the source code tag in favour of the DOM.
An essential example with rel=“nofollow”
A particular instance was extremely helpful. When link-level nofollow properties were added to the source code and the DOM, we wanted to see how Google would respond. We also built a control that had nofollow completely disabled.
The link was ignored thanks to the nofollow directive in the original code. Nofollow in the DOM did not function (the link was followed, and the page was indexed). Why? Because Google has crawled the link and queued the URL before it performed the JavaScript method that inserts the rel=”nofollow” tag – the a href element in the DOM was modified too late. However, if the full a href element with nofollow is added to the DOM, the nofollow is recognised together with the link (and its URL) and is therefore respected.
Outcomes
In the past, ‘plain text’ content has been the main focus of SEO suggestions. AJAX, JavaScript links, and dynamically generated content have all harmed SEO for the major search engines. Clearly, Google is no longer in that position. Although we do not know what is going on in the algorithms behind the scenes, JavaScript links function similarly to ordinary HTML links.
- JavaScript redirects are treated similarly to 301 redirects.
- The processing of dynamically added material, including meta signals like rel canonical annotations, is the same whether it is fired in the HTML source code or after the initial HTML has been parsed with JavaScript in the DOM.
- Google now seems to render the page completely and recognises the DOM rather than simply the raw code. Absolutely amazing! (Remember to provide Googlebot access to those JavaScript resources and external files.)
Google has grown at an incredible rate, leaving the competition in the dust. If other engines want to remain competitive and relevant in the future web development environment, which only means more HTML5, more JavaScript, and more dynamic websites, we expect to see the same sort of innovation from them.
It would be wise for SEOs who have not kept up with the underlying ideas and capabilities of Google to research them and update their consulting to take into account modern technology. You can be overlooking half of the picture if the DOM is not taken into consideration.