MAU – what is metric Monthly Active Users and how is it calculated?
Monthly Active Users (MAU) represent the count of unique users who interact with your app or website over a 30-day period. Unlike Daily Active Users (DAU), which is more applicable for apps that expect daily interaction, MAU is commonly used by apps in industries such as travel or finance, where users engage a few times a month or less, such as banking apps.
What does MAU (Monthly Active Users) mean?
MAU is a metric that provides insights into the number of distinct users who engage with your app or website within a defined 30-day timeframe. Brands typically track MAU using unique identifiers like user IDs, usernames, or emails.
The definition of an active user can vary based on the vertical or business requirements of a brand. To gain a comprehensive understanding of user engagement, it’s important to analyze MAU in conjunction with DAU.
Let’s explore the three components that contribute to MAU calculation:
- Users: When calculating MAU, a user must engage in an in-app action within a 30-day period, such as logging in, completing specific actions, or performing a certain number of actions. Each unique user is counted only once, regardless of the number of logins.
- Action: The specific actions that qualify a user as an MAU are determined by your business. Typically, opening the app or logging in is considered sufficient for measurement and comparison purposes.
- Time frame: MAU is calculated based on either the last month or the 30 days leading up to a specific event or date.
How to calculate MAU (Monthly Active Users) as a metric?
While calculating Monthly Active Users (MAUs) may initially seem straightforward, its complexity can increase based on how the activity is defined.
To calculate monthly active users (MAU), follow these steps:
- Define your criteria for an active user: While a simple log-in can be measured easily, it may not provide sufficient information about whether the user actually engaged with your app. Consider defining an active user as someone who performs a specific in-app action. The more precise your definition, the clearer the data will be when tracking MAU growth or decline.
- Determine the frequency of engagement you want to measure: In this case, it is MAU. Decide how frequently you expect users to engage with your app within a month.
- Collect the data using your preferred analytics tool: Use your chosen analytics tool to gather the necessary data. Identify the number of unique users who meet your criteria for being an active user on a selected day and then for the entire month. Remember, the goal is to measure unique users only, not repeated actions.
By following these steps, you can effectively calculate MAU and gain valuable insights into user engagement with your app over a 30-day period.
Why should you monitor Monthly Active Users (MAU)?
Monitoring monthly active users (MAU) is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it provides valuable insights into how users interact with your app, which is essential for assessing its growth. A high MAU typically indicates a healthy level of app engagement and positive user retention over time.
By measuring MAU, you can effectively evaluate the effectiveness of your marketing strategies and customer experience. It serves as an important indicator of your app’s overall health and can help you identify areas for improvement.
In combination with other engagement-related metrics, monitoring MAU allows you to assess various aspects, including:
- App engagement
- Success rates of specific marketing campaigns (user acquisition)
- Retention rate
- Churn rate
- Growth rate (current and potential)
- Revenue growth rate (current and potential)
Moreover, MAU serves as the foundation for other metrics like lifetime value (LTV) and cost per action (CPA). However, it’s important to note that while MAU provides an indication of your app’s perceived value, there are numerous other factors that contribute to its overall value, such as installs, average revenue per user (ARPU), retention, churn, and purchase frequency.
DAU/MAU ratio (Daily Active Users vs Monthly Active users ratio)
The DAU/MAU ratio provides a measure of the proportion of daily active users (DAUs) to monthly active users (MAUs) who engage with your app within a 24-hour time frame.
This ratio is valuable for forecasting traction and potential revenue over time. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in assessing the perceived value of your product to users by measuring their frequency of returning to the app.
Here’s how the DAU/MAU ratio is calculated:
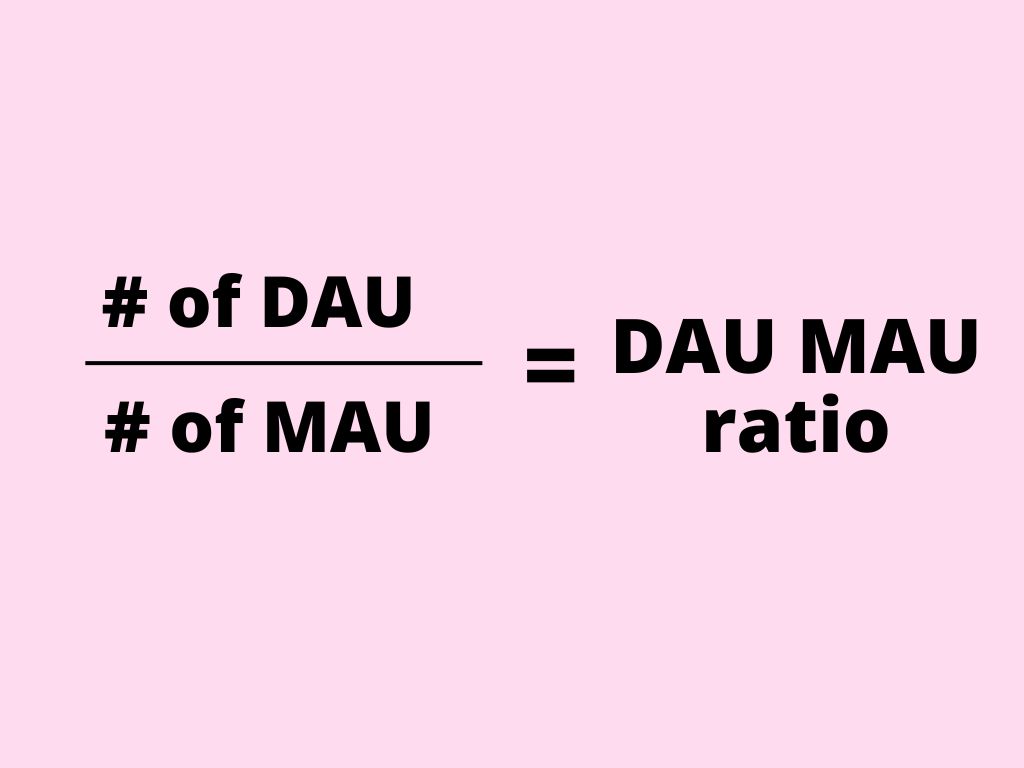
To illustrate, consider the following practical example:
In the month of August, your app had 2,500 DAUs and 10,000 MAUs. The resulting stickiness ratio for that month would be 25%.
Achieving a stickiness average of 20% across industries is considered good, while a ratio of 25% or higher is regarded as exceptional.
Limitations of MAU (Monthly Active Users)
While MAU is a relatively straightforward metric to calculate, it is important to be aware of its limitations. Here’s a brief overview of the main four:
- Lack of industry standardization: One significant limitation of using MAU for comparative analysis is the lack of industry standardization. Different companies employ their own terminologies and methodologies to calculate MAU, making it challenging, and some argue deceptive, to use MAU for meaningful comparisons. The absence of uniform standards for the individual components of MAU makes it a somewhat elusive target.
- The unreliable metric for young businesses: Relying heavily on MAU during the early stages of launching a new app can be problematic. Given the nature of MAU, promotional activities associated with the app launch, such as paid ads and social media campaigns, can inflate MAU figures significantly without reflecting a true trend indicative of steady growth. It is advisable to assess MAU once traffic has normalized over a few months to obtain a more accurate representation.
- Lack of depth of usage measurement: Simply logging into an app does not guarantee user engagement. From a monetization perspective, the users who actively engage with the app are the ones that can be effectively monetized. This makes MAU a somewhat superficial metric when considered as a standalone figure, as it does not provide insights into the depth of user engagement.
- Absence of user quality measurement: Not all users are equal in terms of their value and engagement behavior. Different media sources used for user acquisition may attract users with varying engagement levels. While certain regional campaigns may result in a high number of rapid installs, the associated users may exhibit poor engagement or lead to a sudden increase in churn. Therefore, even if MAUs appear substantial for a specific campaign, the quality of acquired users could be subpar, potentially damaging brand reputation, app store ratings, social media reviews, and overall customer satisfaction.
It is important to consider these limitations and complement the MAU metric with additional measures to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of an app’s performance and user dynamics.
How to increase Monthly Active Users (MAU)?
To effectively increase your monthly active users (MAU) and enhance app engagement, it’s essential to adopt a comprehensive strategy that utilizes multiple channels. Here are some tips and pointers to help boost your MAU rates:
- Push notifications: Push notifications can be highly effective for engaging app users, but they should be used judiciously to avoid generating uninstalls. Focus on providing actual value to your audience rather than bombarding them with frequent notifications. Personalize and tailor your push notifications to improve user experience and track the statistics to understand what resonates with your users.
- In-app messages: Aligning your app experience with users’ needs and preferences increases the likelihood of continued app usage. Research indicates that brands using personalized in-app messages achieve higher retention rates compared to generic campaigns. Use in-app messages to provide important notifications such as app issues, payment failures, or version upgrades. Segment your audience based on regions, preferences, usage, or history to deliver tailored messages with real-time updates and links to personalized content.
- Emails/SMS: Retaining users and keeping your app top of mind requires serving them well and maintaining regular engagement. Utilize email campaigns to support user onboarding as an ongoing process. Target users who were previously active but have become less engaged, sending occasional emails with exciting updates and useful information. For content apps, sending emails with links to trending articles can re-engage users. Proper audience segmentation is crucial in transitioning idle users to engaged users.
- Deep linking: When utilizing channels like emails with specific offers or promotions, ensure a seamless user experience by implementing deep linking. Deep linking allows you to direct users to relevant content within your app rather than simply sending them to the general home screen. By seamlessly integrating different channels and providing a cohesive user experience, deep linking reduces obstacles along the user journey and strengthens user engagement. Implement deep linking as part of your cross-channel strategy to build lasting relationships with users and gain a competitive edge.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively increase your MAU and create a more engaged user base for your app.
Key information about MAU (Monthly Active Users) to remember
- Definition of an active user: The definition of an active user can vary across different business sectors and goals. While commonly considered as a user logging into their account, the specific types of engagement that constitute an active user may differ.
- Assessing campaign effectiveness: Tracking the number of active users over time allows you to evaluate the success of your campaigns and the overall customer experience provided by your app.
- Quantity vs. quality: MAU represents the number of users but does not indicate their quality. In many cases, a small portion of MAU users generates the most value, while others may have lower levels of engagement.
- Comparative challenges: Due to variations in defining an active user, comparing the success of different brands based solely on MAU can be challenging. However, when combined with other metrics, MAU provides insights into app engagement, user acquisition, retention rate, churn rate, and growth rate.
Monitoring MAU alongside other relevant metrics can provide a more comprehensive understanding of your app’s performance and user dynamics.
Was this article helpful?
Support us to keep up the good work and to provide you even better content. Your donations will be used to help students get access to quality content for free and pay our contributors’ salaries, who work hard to create this website content! Thank you for all your support!
Reaction to comment: Cancel reply