
Ultimate SEO Guide – how to fix search engine blacklist by McAfee, Bing, Yandex, Norton or MalwareBytes
Being blacklisted by a search engine is a prevalent issue for websites engaged in malicious internet activities.
We have crafted an insightful piece on Google blacklisting, detailing the process of shedding the blacklist status according to Google’s protocols. It’s advisable to peruse that article subsequent to this one, as the current discussion lays the groundwork by defining what blacklisting entails and how various search engines identify and flag a website as dangerous.
Blacklisting by main leading search engines
Drawing from a legal glossary, a blacklist typically refers to a roster of individuals or entities singled out for exclusion or avoidance. In the digital realm, ‘blacklist’ signifies a website found to host malicious content or reroute visitors to harmful URLs.
Malware could be hidden behind seemingly innocuous hyperlinks or be invisible to search engine crawlers while still executing harmful actions. Numerous search engines deploy crawlers to catalog web pages. If a crawler encounters suspicious elements on a site, it earmarks the site for its blacklist repository. Here’s an exploration of the various forms of blacklisting encountered online:
Google’s search engine blacklist
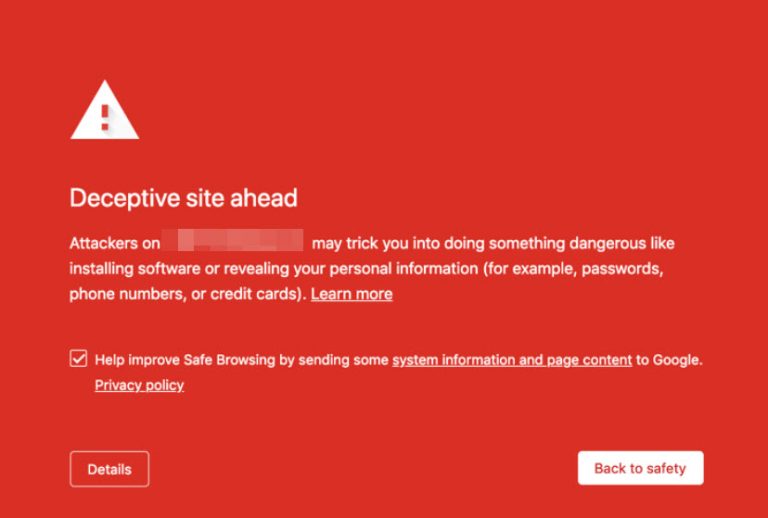
Google SafeBrowsing Alert in Chrome
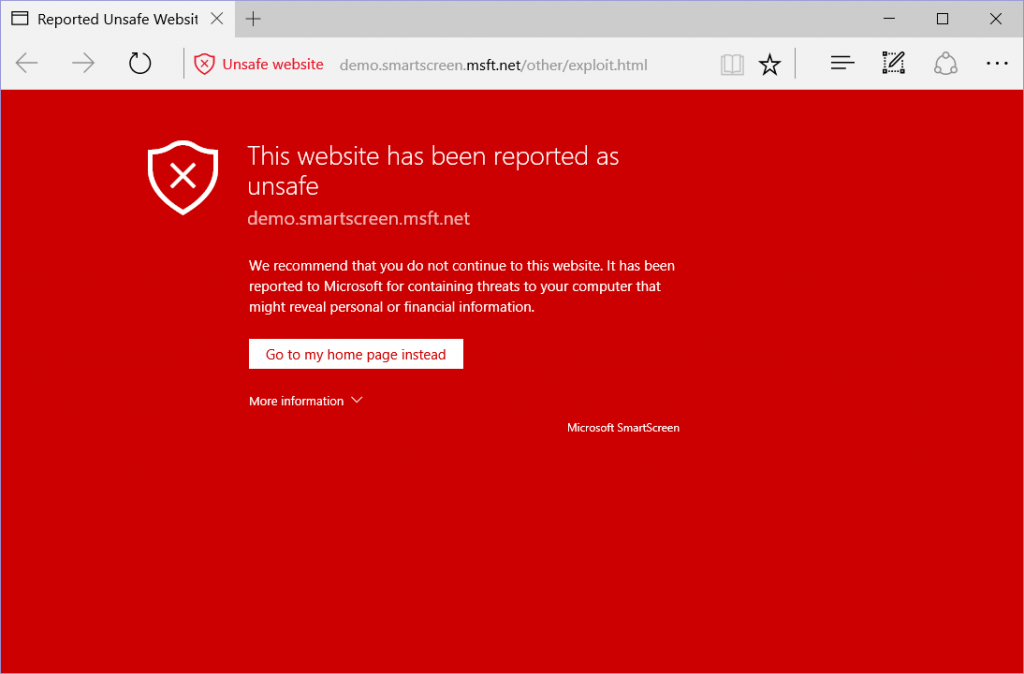
Unsafe website warning in Microsoft Edge
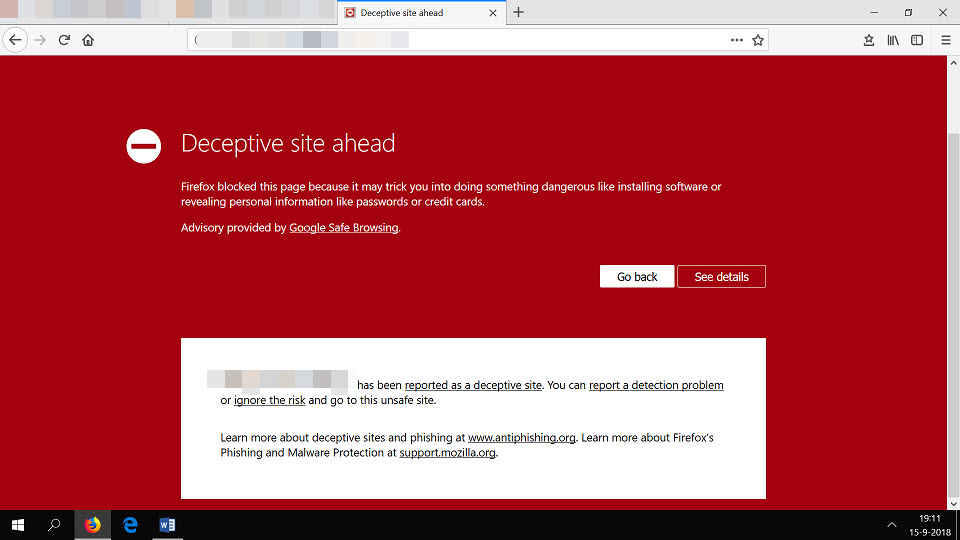
Unsafe website warning in Firefox
These warnings can also appear in a number of different ways in search results:

Google SERP indicating “This site may be hacked.”
Understanding blacklisting criteria Google, as the foremost search engine, will blacklist a website if it detects malware or signs of phishing activities. Its crawlers are designed to spot any malicious scripts activated by hyperlink engagement on the site.
Redirects leading to dubious or insecure domains are also grounds for blacklisting. Consequently, users attempting to visit the affected website will encounter the cautionary message “This site may harm your computer.”
Google proactively notifies website owners if their site has been blacklisted, enabling them to take corrective actions to resolve the issues. Additionally, Google may blacklist a site if it exhibits traits of phishing, such as web pages designed to collect sensitive user information that is then transmitted to servers managed by hackers. Consequently, if a website is found to have such phishing attributes, it may be flagged and blacklisted.
Search engine blacklists: Yandex’s approach to blacklisting
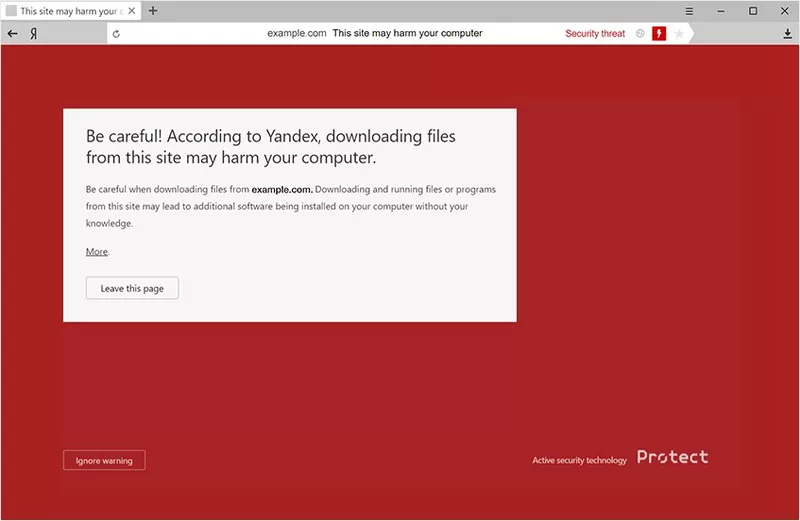
A warning is shown by Yandex for a blacklisted website
For those unfamiliar, Yandex is the leading search engine in Russia and the Netherlands. Yandex Safe Browsing is a service that blacklists websites deemed unsafe for various reasons, including:
- Detection of malicious code on the site.
- Classification of the website as undesirable.
- Constant safety warnings to users attempting to access the site.
- Discrepancies between the site’s code and the backup or control system version, particularly if the code is unreadable or unstructured.
- The presence of malicious functions within the website’s structure.
- Modification dates of files aligning with the dates of malicious data infection.
- The website’s failure to appear in Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) upon being searched.
- Opera browser also employs the same algorithm for its safety measures.
Search engine blacklist: Bing’s criteria for blacklisting
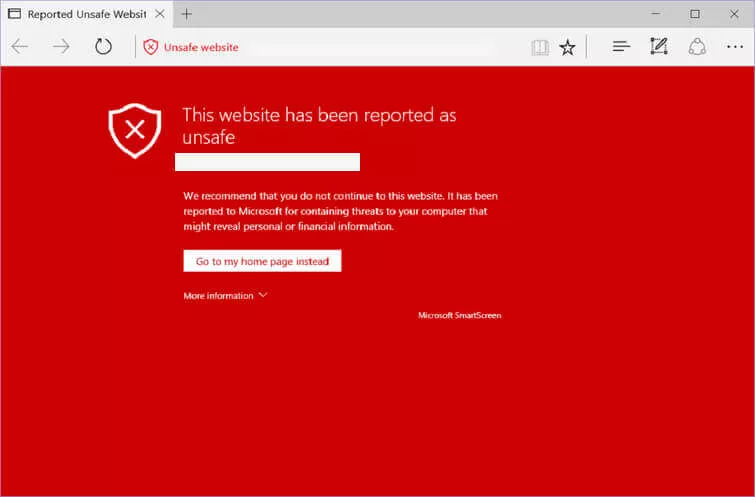
A warning is shown by Bing for a blacklisted website
The blacklist for Bing search engine is managed by Microsoft, which bases its blacklisting criteria on the number of deep links a website has when it is searched within the search engine.
Blacklisting by antivirus firms
Antivirus firms play a crucial role in internet safety by identifying and blacklisting websites that pose a threat to users. These companies employ sophisticated scanning technologies to evaluate websites across a spectrum of security parameters. Here’s how some of the leading antivirus companies approach the task of blacklisting potentially harmful sites.
Norton’s blacklisting process
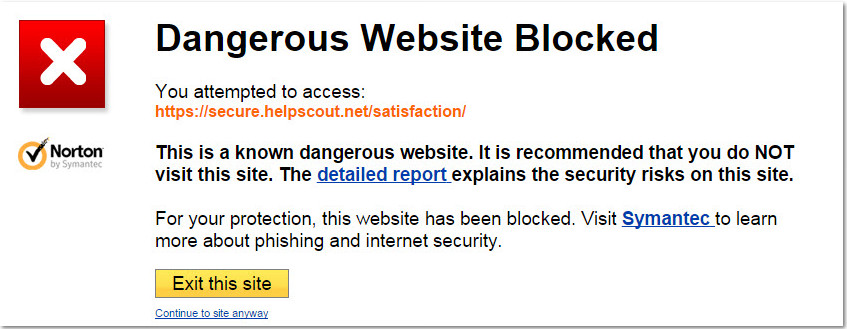
A blacklisting warning message by Norton
Norton safeguards internet users through its website rating service, which assesses the safety of websites. Website owners can submit their sites to Norton using a specific form. Norton’s crawlers then evaluate the site based on several criteria, including the presence of malware, malicious JavaScript and iFrames, drive-by downloads, anomalies, Internet Explorer-only attacks, suspicious redirections, and spam. Based on these evaluations, Norton determines whether a website is safe or malicious.
Norton employs a rating service to evaluate websites. Site owners must submit their site through Norton’s provided form, after which Norton’s crawlers assess the site based on several criteria, including:
- Presence of malware
- Malicious JavaScript and iFrames
- Drive-by downloads
- Anomalies
- IE-only attacks
- Suspicious redirections
- Spam
Following this evaluation, a determination is made regarding the site’s safety.
McAfee’s approach to blacklisting
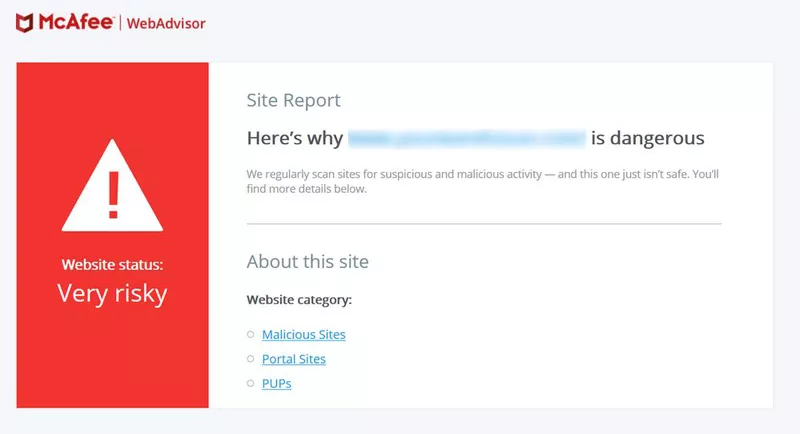
A blacklisting warning message by McAfee
McAfee Web Advisor acts as a browsing companion, enhancing security by offering features beyond malware and phishing detection. These include typo protection, download scanning, and firewall functionality checks, aiming to secure the user experience online.
McAfee enhances browser safety with its Web Advisor tool, acting as a security companion for users online. Beyond detecting and blocking malware and phishing attempts, Web Advisor offers typo protection, scans downloads for safety, and verifies firewall functionality. This multifaceted approach ensures a more secure browsing experience, warning users before they interact with potentially dangerous websites.
MalwareBytes’ blacklisting criteria
MalwareBytes blacklists websites linked to malicious IPs or servers. However, due to instances of false positives, reliance solely on MalwareBytes for blacklisting status is not advised.
The impact of being blacklisted
Being blacklisted can drastically reduce your website’s traffic, potentially leading to a 95% decrease. This significant drop can severely affect a company’s revenue, as user trust diminishes due to concerns over data security. In today’s competitive environment, where having an online presence is crucial for business growth, maintaining a clean, unblacklisted website is imperative. Website owners should vigilantly monitor for and rectify any malicious content or links to avoid blacklisting and its detrimental effects.
Steps for website blacklist removal
Let’s explore strategies to prevent your website from being blacklisted and how to address issues if your site is already affected.
- Eliminating malware from files – as a site administrator, having the capability to alter server-hosted files is crucial for removing malware infections. Consider restoring your site using previous, uninfected backups. If you’re removing malicious files directly via FTP access, ensure you have a clean backup of your site. If the process of eliminating infected files seems daunting, don’t hesitate to consult with cybersecurity experts.
- Cleaning malware from databases and tables – access your database management panel to tackle infected databases and tables. Ensure you’ve backed up all clean data before proceeding. You can then identify and either delete or isolate the compromised database or table sections. Tools like PHPMyAdmin, provided in most cPanel offerings, simplify this process with a user-friendly interface. Be wary of common malicious PHP functions such as
eval(),base64_decode(),gzinflate(),preg_replace(), andstr_replace(). While these functions might be utilized by legitimate plugins for standard operations, they’re often exploited for malicious purposes. Carefully test any changes to avoid inadvertently disrupting your site’s functionality. - Enhancing security with a robust website firewall – strengthening your website’s firewall can prevent unauthorized access attempts to your admin console, thwarting brute-force attacks. Your site should also have measures in place to detect and mitigate Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks through the early identification of an uptick in false traffic. Additionally, maintaining the highest level of security by regularly patching identified vulnerabilities is essential for keeping your website safe and off blacklists during routine security audits.
Lifting your website ban off Google’s blacklist
If you’re looking to delist your website from Google’s blacklist, here are the steps you should follow:
- Enroll your website with Google Search Console.
- Access the Manual Actions or Security Issues sections within the console.
- Identify the specific URLs that prompted Google to mark your website as malicious.
- Through the admin console, delete the problematic hyperlinks from your site.
- File a delisting request with Google Search Console.
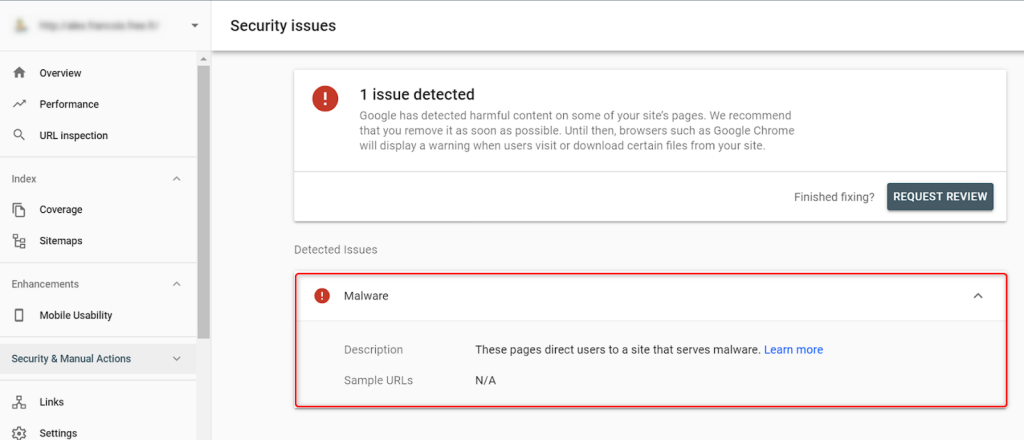
How to remove ban from Google Search Console
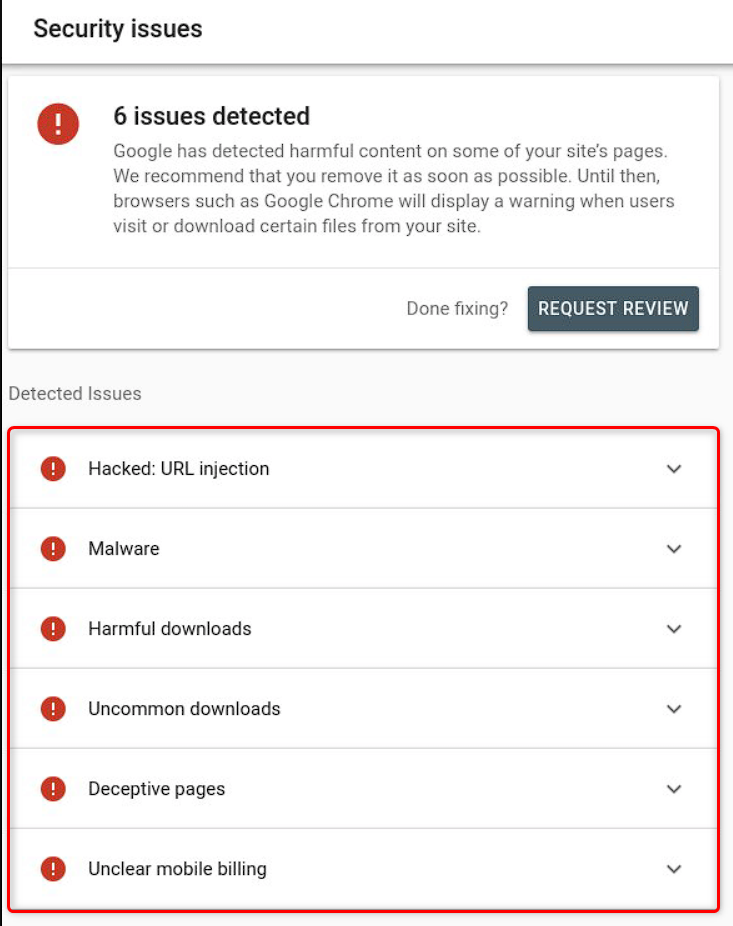
Here you can see all problems detected in Google Search Console
How to solve ban and delisting your website from Yandex’s blacklist
To have your website removed from Yandex’s blacklist, please proceed with the following steps:
- Log into Yandex’s console and register your site.
- Temporarily halt your web server’s operations.
- Perform a comparative scan of both a malicious and a clean, uninfected backup of your website.
- Analyze the scan results for discrepancies and excise any suspicious or malicious code identified.
- Prior to finalizing changes, conduct tests to ensure they don’t disrupt website functionality. If the modifications don’t negatively affect your site, implement the changes and update all related software.
- Reach out to Yandex Webmaster with a request to remove your site from the blacklist.
Getting your website off McAfee’s blacklist
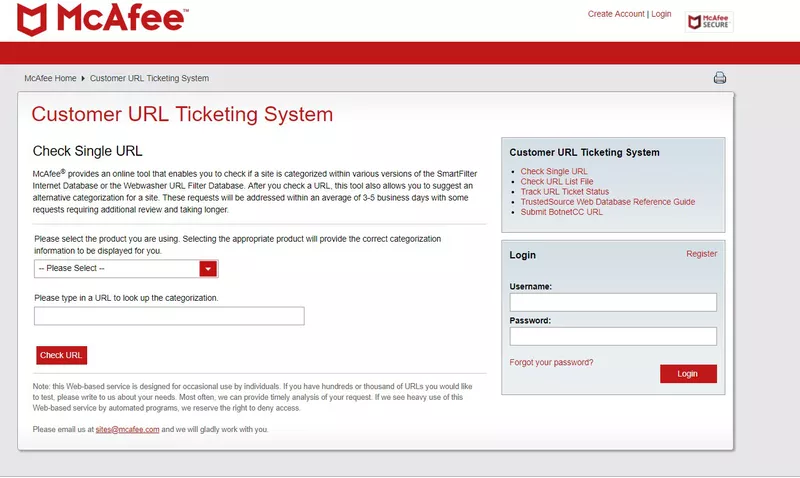
McAfee trusted source blacklist removal window
If you find your website listed on McAfee’s blacklist, here are the steps to follow for removal and to regain trust:
- Visit McAfee TrustedSource and log in.
- Choose the appropriate category for your website from the drop-down menu. The database is updated in real time, ensuring the information is current.
- In the comments section, detail the corrective actions you’ve undertaken, such as eliminating malware from specific files, implementing a Web Application Firewall, etc.
- Provide an email address where you’d like to receive notifications regarding the status of your request and submit your removal petition.
In conclusion, blacklisting represents a significant challenge in the competitive landscape of modern business. Needless to say, a secure website not only attracts more visitors but also converts them into clients. Therefore, adopting proactive measures to safeguard your website is essential. The most effective approach involves selecting a security solution that offers continuous monitoring and preemptive protection against infections, ensuring your website remains clean and trustworthy.
Was this article helpful?
Support us to keep up the good work and to provide you even better content. Your donations will be used to help students get access to quality content for free and pay our contributors’ salaries, who work hard to create this website content! Thank you for all your support!
Reaction to comment: Cancel reply